The Future of Cloud Computing
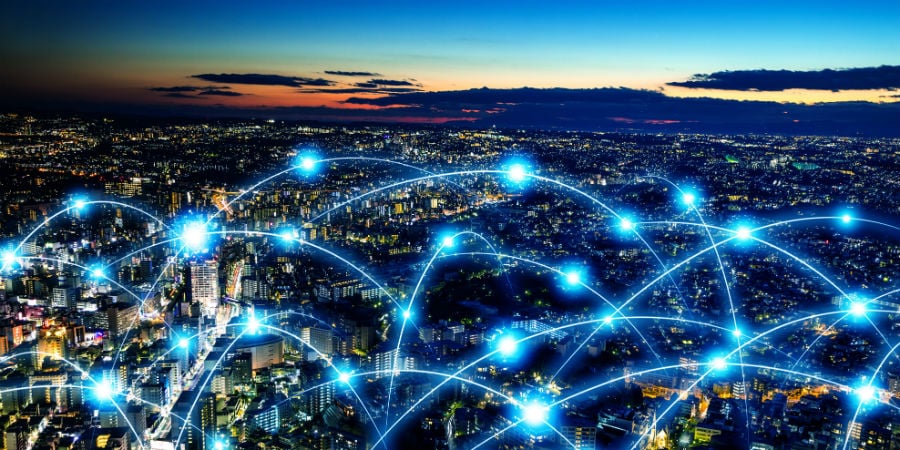
The Future of Cloud Computing
What is Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services, including storage, processing 09 power, software applications, and databases, over the internet. Instead of relying on local servers or personal computers to store and process data, cloud computing utilizes a network of remote servers hosted on the internet to provide these services.
In cloud computing, users can access and use these services on-demand, paying only for the resources they consume. The cloud infrastructure is typically owned and maintained by a cloud service provider, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These providers offer a range of services, including Infrastructure as a Service (laaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
The Future of Cloud Computing:
As we look to the future, cloud computing continues to evolve and shape the way businesses operate and innovate. Here are some key trends and predictions that offer insights into the future of cloud computing:
- Hybrid and Multi-cloud Environments: Organizations are increasingly adopting hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, combining private and public clouds as well as utilizing multiple cloud providers. This allows them to leverage the strengths of different cloud platforms and achieve better flexibility, scalability, and cost optimization
- Edge Computing: As the demand for real-time processing and low-latency applications increases, edge computing is gaining prominence. Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source, reducing the need for centralized cloud infrastructure. It enables faster response times, bandwidth optimization, and improved security and privacy.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless computing, also known as Function as a Service (FaaS), is expected to gain popularity. It allows developers to focus on writing and deploying code without worrying about managing servers or infrastructure. Serverless architectures offer scalability, cost efficiency, and reduced operational complexity
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Cloud platforms are becoming the go-to choice for Al and ML workloads due to their computational power, scalability, and access to vast amounts of data. Cloud providers are investing heavily in Al and ML services, making it easier for developers to build and deploy intelligent applications.
- Quantum Computing: While still in its early stages, quantum computing holds the potential to revolutionize cloud computing. Quantum computers can solve complex problems much faster than classical computers. Cloud providers are exploring quantum computing as a service to enable businesses to leverage its power without the need for expensive infrastructure.
- Enhanced Security and Privacy: With increasing concerns about data breaches and privacy regulations, cloud providers are focusing on enhancing security and privacy measures. This includes advancements in encryption, secure access controls, and compliance with data protection regulations.
- Serverless Containers: The combination of serverless computing and containerization is gaining traction. Serverless containers provide an abstraction layer that simplifies the deployment and management of containerized applications, offering improved scalability and efficiency.
- Green Cloud Computing: As environmental sustainability becomes a priority, cloud providers are investing in energy-efficient infrastructure and sustainable practices. This includes using renewable energy sources, optimizing data center cooling systems, and reducing carbon footprints.
- Data Analytics and Insights: Cloud platforms provide extensive capabilities for data storage, processing, and analytics. The future will see advancements in cloud-based data analytics, including real-time analytics, predictive modeling, and prescriptive analytics, enabling businesses to extract valuable insights from large datasets.
- Continued Innovation: Cloud computing is a rapidly evolving field, and innovation will continue to drive its growth. Cloud providers will introduce new services, features, and technologies to meet the evolving needs of businesses, developers, and consumers.

Benefits of Cloud Computing for Businesses
- Scalability: Cloud computing provides businesses with the ability to scale their resources up or down based on demand. This flexibility allows organizations to easily accommodate growth or handle sudden increases in workload without investing in additional hardware or infrastructure.
- Cost Savings: Cloud computing eliminates the need for upfront hardware investments and the costs associated with maintaining and upgrading on-premises infrastructure. Businesses can pay for cloud services on a pay-as-you-go basis, optimizing costs and avoiding unnecessary expenses.
- Accessibility and Mobility: Cloud services are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work, collaboration, and mobility. Employees can access applications and data on various devices, improving productivity and flexibility.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Cloud computing provides robust backup and disaster recovery solutions. Data is securely stored in multiple locations, reducing the risk of data loss. In case of a disaster, businesses can quickly recover their data and resume operations.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Cloud-based collaboration tools enable real-time collaboration, document sharing, and seamless communication among team members. This facilitates efficient teamwork, boosts productivity and streamlines workflows
- improved security: Cloud service providers implement robust security measures to protect data. They invest in security technologies, encryption, and regular security updates, often surpassing the security capabilities of individual businesses. This ensures data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
- Increased Flexibility: Cloud computing allows businesses to adapt to changing needs quickly. It provides a platform for testing and deploying new applications and services. enabling rapid innovation and reducing time to market.
- Automatic Software Updates: Cloud service providers handle software updates and maintenance, ensuring that businesses have access to the latest features and security patches. This eliminates the need for businesses to manually update their applications, saving time and effort.
- Eco-Friendly: Cloud computing reduces the environmental impact associated with traditional on-premises infrastructure. By leveraging shared resources and optimizing energy consumption, businesses can achieve greater energy efficiency and reduce their carbon footprint.
- Global Presence: Cloud computing enables businesses to expand their operations globally with ease. Cloud providers have data centers located worldwide, allowing businesses to reach customers in different regions and provide a consistent user experience.
Conclusion
The future of cloud computing in our daily lives is evident in multiple areas. It provides secure and accessible data storage, ensuring that personal files, photos, and documents are protected and easily retrievable. Cloud-based collaboration tools enhance productivity and enable real-time teamwork across geographically dispersed teams.
Reference
Here are some ideas for reference content that you can consider: